ACT Science Practice Test 25
Bộ sưu tập: Tuyển Tập Bộ Đề Thi Đại Học Hoa Kỳ (ACT) - Có Đáp Án Chi Tiết
Số câu hỏi: 23 câuSố mã đề: 1 đềThời gian: 1 giờ
205,248 lượt xem 15,785 lượt làm bài
Bạn chưa làm đề thi này!
Phosphorus is an essential nutrient that can negatively affect water quality, primarily by promoting excessive plant and algae growth. When this occurs, plants and animals that live in the water are affected by the reduced sunlight and lower oxygen levels that develop as organic matter decomposes. For humans, algal blooms lead to a reduction in the quality of drinking water, a decrease in the use of the water source for recreational activities, and a decline in property value along waterfront areas.
Lakes are often classified according to their trophic state, which indicates their biological productivity. The least productive lakes are called oligotrophic. Bodies of water classified as oligotrophic are typically cool and clear, have relatively low nutrient concentrations, and provide excellent drinking water. The most productive lakes are called eutrophic and are characterized by high nutrient concentrations that result in algal growth, cloudy water, and low dissolved oxygen levels. Table 8.6 shows the phosphorus levels that are found in lakes with different trophic classifications.
TABLE 8.6

Lake managers collected data over approximately two decades in four different ecological areas of a large lake. Each area had a different target phosphorus level based on the natural ecological factors of the area, as indicated in Figures 8.7 through 8.10. For proper lake health, the level must be at or below the target amount. Levels in excess of the target amount lead to an imbalance in nutrient flow.
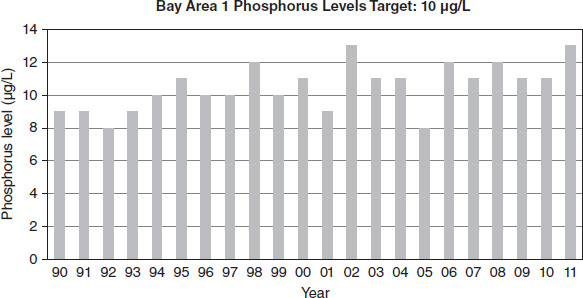
Figure 8.7
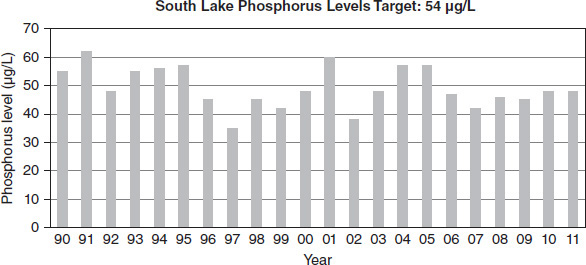
Figure 8.8
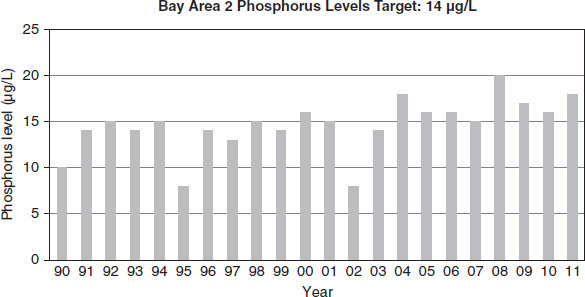
Figure 8.9
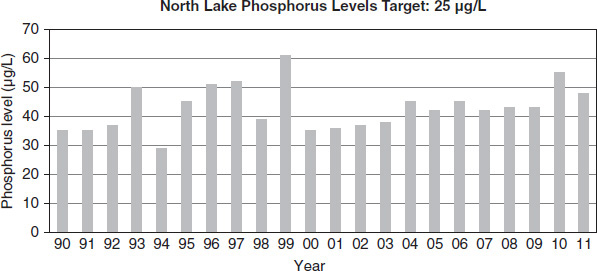
Figure 8.10
In which area of the lake did the scientists fail to attain the target phosphorus level in any of the years of the study?
Bay Area 1
North Lake
Bay Area 2
South Lake
The target for Bay Area 2 falls in the trophic category of:
oligotrophic.
mesotrophic.
eutrophic.
hypereutrophic.
In 2011, flooding occurred in the region surrounding the lake. This caused:
all areas of the lake to exceed their target phosphorus levels.
all areas of the lake to meet the standard for target phosphorus level.
all but one of the lake areas to exceed the recommended phosphorus levels.
two of the four lake areas to exceed the target phosphorus level.
In 2005, ecologists managing the lake began a concentrated effort to reduce agricultural runoff. This appears to have had the greatest effect on phosphorus levels in:
Bay Area 1.
North Lake.
Bay Area 2.
South Lake.
In 2002, the South Lake area had a trophic classification of:
oligotrophic.
mesotrophic.
eutrophic.
hypereutrophic.
For how many years of the study was Bay Area 2 found to be mesotrophic?
0
3
9
19
During which of the following years did Bay Area 1 have a trophic classification of mesotrophic?
1992
1995
2009
2011
Which of the following best describes the range in phosphorus levels in the North Lake over the 21-year period?
32 μg/L
62 μg/L
25 μg/L
45 μg/L
Which lake had the narrowest range of phosphorus levels over the time period of the study?
Bay Area 1
North Lake
Bay Area 2
South Lake
During how many years did Bay Area 1 meet or surpass the standard for proper lake health?
4
10
10
15
What was the difference in phosphorus concentration between Bay Area 1 and North Lake in 1993?
9 μg/L
41 μg/L
50 μg/L
59 μg/L
A neighboring lake was tested in 2005 and found to have a phosphorus level of 10 μg/L. It was most likely taken from a body of water similar to:
Bay Area 1.
North Lake.
Bay Area 2.
South Lake.
Which of the following statements is best supported by the information in the passage and figures?
When studying the North Lake area, one would expect to find cool, clear water and high oxygen levels.
None of the target levels for any of the lake areas fell in the eutrophic category.
The management of phosphorus levels does not have a positive impact on humans who use the lake for recreation.
During the 21-year period of the study, none of the lakes could be classified as hypereutrophic.
The category of lake classification appearing most frequently in the North and South Lake areas was:
oligotrophic.
mesotrophic.
eutrophic.
hypereutrophic.
According to the information provided in the passage, which of the areas was the most likely to have the lowest dissolved oxygen levels in 2010?
Bay Area 1
North Lake
Bay Area 2
South Lake
There is some evidence that ancient civilizations knew placing various metals together could create an electrical current. In the year 1800, Alexander Volta published experiments outlining his discovery of the voltaic pile, a device commonly referred to as the first electric battery. Volta stacked two different metals on either side of a wet felt disk and found that certain combinations produced an electrical voltage. By the early 1800s, many scientists were expanding on the idea of the voltaic pile by making apparatuses now known as voltaic cells. These cells generally contain two separate jars connected by a salt bridge, or porous membrane. Each jar contains a certain metal and a solution of the positive ions of the same metal. When different jars containing different metals are connected, an electrical voltage can be produced. A theoretical example of a copper/zinc voltaic cell is shown in Figure 9.1.
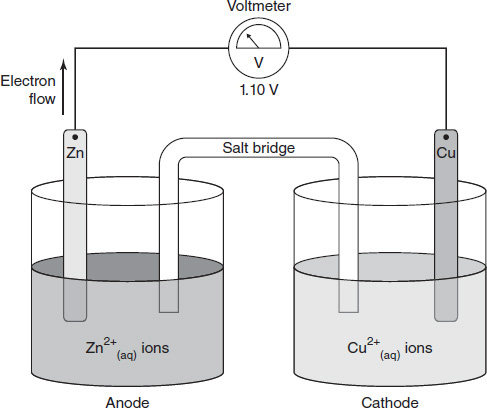
Figure 9.1
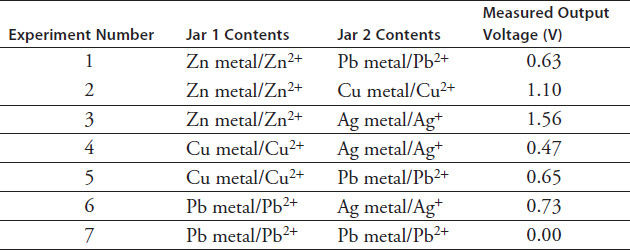
The last two centuries have seen a marked spike in demand for smaller batteries that can produce higher voltages for longer periods of time. This led a chemistry student to become interested in how using different metals in the voltaic cell could increase the voltage output of that cell. To conduct the experiment she chose four different types of metals that were available in strips from her local hardware store. These metals were zinc (Zn), lead (Pb), copper (Cu), and silver (Ag). She used 1-molar concentrated solutions of each of the various metal ions. She then made a salt bridge out of filter paper soaked in a potassium chloride brine solution. Many different combinations of metals were attempted, and the voltage output was measured with a standard voltmeter. The results of the experiment are recorded in Table 9.1.
TABLE 9.1
After the experiment was completed, the chemistry student looked at the literature to make sense of her results. She found two definitions particularly helpful. The anode was defined as the metal strip where oxidation occurs. The metal atoms were losing electrons and dissolving into the solution as metal ions. Electrons from the anode were free to move through the wire toward the cathode. The cathode was defined as the metal strip where reduction occurs. The cathode had an abundance of electrons from the anode. Metal ions in the solution around the cathode accepted those electrons and joined the strip as additional solid metal atoms.
The student also found tables of standard reduction potentials (Table 9.2). These tables compared how much voltage should be produced when the metal is placed in an electrochemical cell with a standard electrode. One table showed each metal as a cathode, and the other showed each as an anode. The student learned that these tables were used to calculate the theoretical voltage output of any electrochemical cell. (Any electrochemical cell has to have both a cathode and an anode.)
TABLE 9.2
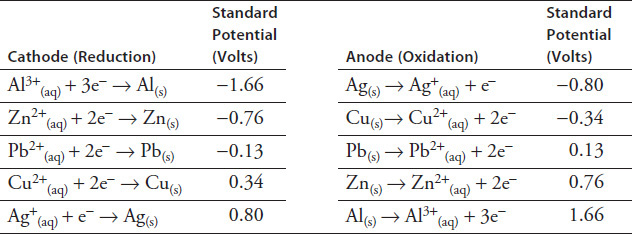
The theoretical output voltage of an electrochemical cell is the sum of the standard potentials of the anode and the cathode.
Which of the following best describes the independent variables of this investigation?
The types of metal used for the cathode and anode
The type of metal ion solution used in the anode jar
The amount of output voltage produced by various electrochemical cell configurations
The concentration of metal ion solution used in each electrochemical cell
Which variable should not be controlled for this experiment?
The surface area of the metal strip used for the anode
The type of metal strip used for the anode
The amount of time the electrochemical cell is allowed to operate
The concentration of potassium chloride used to make the salt bridge
A lead/silver electrochemical cell is expected to have an output voltage of 0.93 V. However, Experiment 6 from Table 9.1 shows a measured output voltage of 0.73 V. Which of the following might account for the difference?
Silver should have been the cathode, and lead should have been the anode, but the experimenter switched them.
Experiment 6 was the third time the silver ion solution had been used, and the concentration of silver ions had been diminished.
The experimenter mistakenly switched a lead strip with a zinc strip for the anode.
The experimenter used a 1.5-inch-wide strip of lead as the anode instead of the standard 1-inch strip.
Experiment 1 from Table 9.1 shows a zinc/lead cell with a measured output voltage of 0.63 V. Which of the following best describes the cell?
Zinc is the cathode and lead is the anode.
Zinc is the cathode and zinc ions are the anode.
Zinc is the anode and lead is the cathode.
Zinc is the anode and zinc ions are the cathode.
Figure 9.1 shows the electrochemical cell the student used for Experiment 2 where zinc was the anode and copper was the cathode. What can be inferred about the mass of the zinc and copper strips as the experiment progressed?
The mass of both strips increased.
The mass of both strips decreased.
The mass of the zinc strip increased, but the mass of the copper strip decreased.
The mass of the zinc strip decreased, but the mass of the copper strip increased.
Experiment 8 was conducted with an aluminum strip in Jar 1 and a copper strip in Jar 2. Which metal would be the anode?
Aluminum would be the anode.
Copper would be the anode.
Aluminum would be the anode until the metal dissolved to a certain point, and then copper would become the anode.
There is not enough information to determine which would be the anode.
Experiment 8 was conducted with an aluminum strip in Jar 1 and a copper strip in Jar 2. What would be the expected output voltage of the electrochemical cell?
1.10 V
1.66 V
1.32 V
2.00 V
Further experimentation finds that when electrochemical cells are hooked together in a series configuration, their output voltage is added together for total output voltage. How many copper/zinc electrochemical cells are required to light a diode that needs a minimum of 12.0 V to operate?
2 cells
10 cells
11 cells
12 cells
1 mã đề 55 câu hỏi
1 mã đề 23 câu hỏi
1 mã đề 10 câu hỏi
1 mã đề 24 câu hỏi
1 mã đề 22 câu hỏi

