ACT Science Practice Test 21 - Multiple Choice Questions
Từ khoá: act science act practice test act science practice test 21 luyện thi act đề thi act online act multiple choice act science section act exam preparation
Bộ sưu tập: Tuyển Tập Bộ Đề Thi Đại Học Hoa Kỳ (ACT) - Có Đáp Án Chi Tiết
Số câu hỏi: 25 câuSố mã đề: 1 đềThời gian: 1 giờ
213,903 lượt xem 16,448 lượt làm bài
Corals build the habitat that is the home for the fish and other marine species that live on the reef. The corals grow by creating aragonite forms of calcium carbonate cups in which the polyp sits. Figure 6.11 identifies the anatomy of a coral polyp.
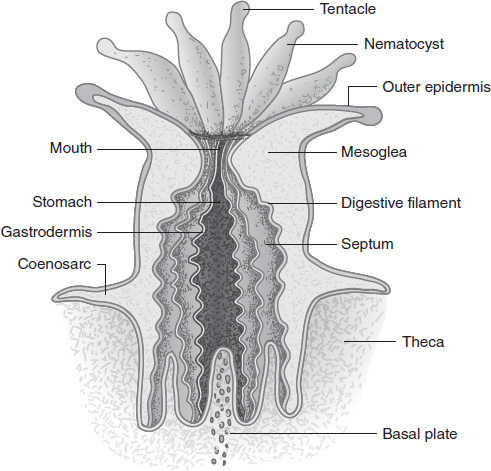
Figure 6.11
Source: http://oceanservice.noaa.gov/education/kits/corals/media/supp_coral01a.html.
Millions of photosynthetic algae, called zooxanthellae, reside inside polyp tissues. They serve as an energy source for corals as well as providing the coloration for which corals are known.
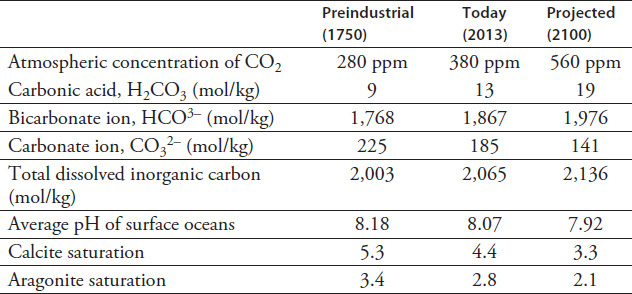
Current research indicates that increasingly acidic waters may be to blame for the decline in coral populations. Oceans absorb atmospheric carbon dioxide. Table 6.2 depicts changes to ocean chemistry and pH estimated using scientific models calculated from surface ocean measurement data.
TABLE 6.2 Ocean Chemistry and pH
Some coral become less successful at reproducing sexually in acidic waters. Studies also show links between ocean acidification and coral bleaching. Figure 6.12 summarizes the physiological responses of marine organisms to biological ocean acidification experiments done by various scientists.
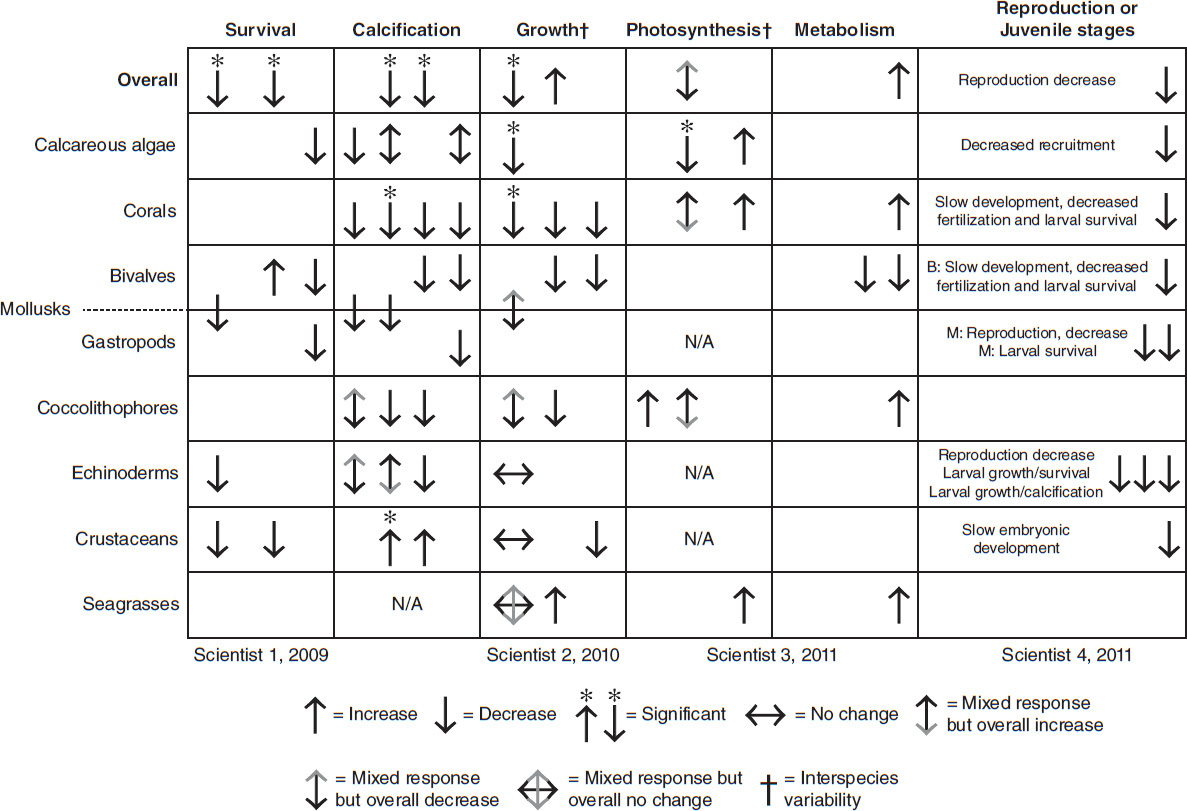
Figure 6.12
Source: Data adapted from "Recognising Ocean Acidification in Deep Time: An Evaluation of the Evidence for Acidification across the Triassic-Jurassic Boundary," Sarah E. Greene, Rowan C. Martindale, Kathleen A. Ritterbush, David J. Bottjer, Frank A. Corsetti, and William M. Berelson, Earth-Science Reviews, volume 113 (1-2), copyright © 2012 by Elsevier.
Zooxanthenellae would logically inhabit which part of a coral?
Stomach
Basal plate
Outer epidermis
Stinging nematocyst
The data in Table 6.2 indicates that as the concentration of carbon dioxide in the water rises:
the pH decreases and the balance shifts toward bicarbonate instead of carbonate.
the pH increases and the carbonate ion concentration increases.
both the pH and the bicarbonate concentration decrease.
the pH increases and the balance shifts toward carbonate instead of bicarbonate.
Based on the information in Table 6.2, what conclusions can be drawn about ocean chemistry?
Future emissions of carbon dioxide are less likely to significantly impact ocean chemistry over time.
Increased atmospheric carbon dioxide will have little impact on the concentration of carbonate ions.
Chemical changes in oceans are a result of the water absorbing atmospheric carbon dioxide produced by human activities.
Ocean acidification is an unpredictable response that is unlikely to be linked to human activities that increase the atmospheric concentration of carbon dioxide.
Factors that might impact the data found in Table 6.2 include:
I. seasonal changes in temperature.
II. variations in photosynthesis.
III. runoff from rivers.
IV. fluctuations in respiration.
Which of these is likely to account for fluctuations in the geographic pH of ocean waters?
II
III
I and IV
II and III
The saturation horizon is a natural boundary in seawater, above which calcium carbonate (CaCO3) can form and below which it dissolves. Which species from Figure 6.12 most likely lives below the saturation horizon?
Corals
Gastropods
Crustaceans
Calcareous algae
Calcifying organisms that produce the calcite form of calcium carbonate, such as foraminifera, can be less vulnerable to acidification than those constructed with aragonite structures, such as corals. Which of these provides a logical explanation for these findings?
Aragonite is more soluble than calcite.
Calcite is more soluble than aragonite.
Aragonite saturation is farther from the surface of oceans.
Calcite saturation is farther from the surface of oceans.
Based on the information in Figure 6.12, decreased fertilization affects corals as well as:
echinoderms.
bivalves.
crustaceans.
calcareous algae.
In Figure 6.12, the most significant data with regard to the health of marine ecosystems is:
the decline in coral calcification.
the rise in crustacean calcification.
the declining metabolism of bivalves.
the decreased larval survival in gastropods.
According to Figure 6.12, which species appear to be most affected by ocean acidification?
Echinoderms
Gastropods
Calcareous algae
Crustaceans
Which of the following terms best describes the relationship between zooxanthellae and corals?
Parasitic
Codependent
Symbiotic
Mutualistic
Corals have several features that help them survive in the shallow ocean. Which part of a coral's anatomy may protect against fluctuating environmental changes such as temperature?
Stomach
Nematocysts
Basal plate
Outer epidermis
Some corals can reproduce in a variety of ways. Which of these methods would produce the most diverse offspring?
Coral fragments regenerate to form new coral.
Adult coral sprouts tiny buds to form new coral.
Adult coral divides and both pieces grow new coral.
Coral eggs join with coral sperm to form new coral.
Which of the following is most likely to result from declines in a coral polyp's zooxanthellae population?
Bleaching
Hyperpigmentation
Increased thermal tolerance
Accelerated growth of nematocysts
Scientists design an experiment in an attempt to predict the effect increasingly acidic seawater will have on coral reproduction. They may use the following in the experiment:
- Aquarium tanks
- Seawater
- Tap water
- Corals
- Carbon dioxide bubbles
Which experimental design will allow the scientists to investigate their hypothesis fairly and produce high-quality data for analysis?
Use two tanks filled with seawater and corals. Add carbon dixiode bubbles to one tank.
Use two tanks filled with tap water and corals. Add carbon dioxide bubbles to one tank.
Use two tanks filled with corals. Add tap water to one tank and seawater to the other.
Use three tanks filled with carbon dioxide bubbles. Add tap water and seawater to each tank.
Changes in the biological processes in the surface ocean water affect deeper portions of the ocean because:
habitats at deeper levels depend on dissolved oxygen occurring at the surface.
organisms living at lower ocean levels rely mainly on products created by organisms at shallow levels.
the pH of organisms in shallow waters is altered and becomes non-nutritious to deep-water organisms.
the calcification of shallow-water organisms provides an additional layer of protection that prevents predation.
Lenses are made of transparent materials such as glass and plastic and are used in eyeglasses, cameras, and telescopes, as well as other applications. When light rays enter a curved lens from a distant object, the rays are bent into new angles. A convex lens, which is thicker in the middle, takes parallel light rays and converges them toward a common point called the focal point. The focal length is defined as the distance from the center of the lens to the point where the bent rays converge. A concave lens, on the other hand, is thinner in the middle and diverges parallel light rays as if they came from a point ahead of the lens (this point is one focal length from the lens). Both lenses are shown in Figure 7.1.

Figure 7.1
In conventional ray diagrams, the source of light (the object) is to the left of the lens and the rays move to the right through the lens. Light rays leave objects at various angles and are bent by the lens to form an image of the distant object. Real images are formed when actual light rays converge to a common point to the right of the lens. Virtual images are formed when the observer looks backward through the lens and sees an image on the same side of the lens as the object. Table 7.1 summarizes the images observed by these lenses.
TABLE 7.1
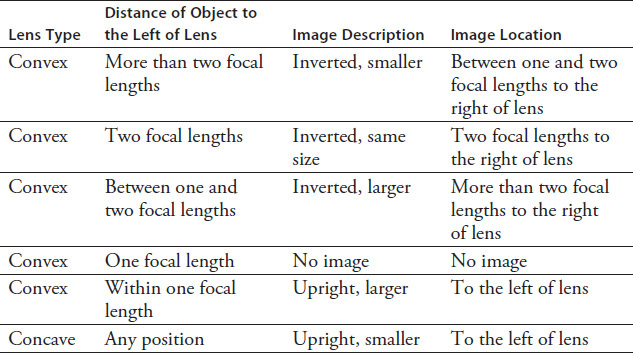
When the human eye views distant objects, the light rays go through a lens that is thicker in the middle. An image forms on the retina, which is the inner back surface of the eye. Which of the following best identifies the eye's lens and the characteristics of the image?
Convex; real, inverted, and smaller
Concave; virtual, upright, and smaller
Convex; virtual, upright, and larger
Concave; real, inverted, and smaller
According to the information provided in the passage and Table 7.1, which of the following statements is true?
A lens that is thinner in the middle is capable of forming inverted images.
Convex lenses form a real image when the object is one focal length to the left of the lens.
Concave lenses can form images with many characteristics.
All real images are inverted.
A particular convex lens in a camera has a focal length of 10 cm. If the object for the picture is 30 cm from the lens, what type of image will form on the film?
A real, inverted, smaller image
A real, inverted, larger image
A real, inverted, same-size image
A virtual, upright, smaller image
Rays of light from the distant sun reach the earth nearly parallel with each other. A child wishes to take these rays of light and use them to burn a piece of paper. What type of lens should the child use, and how far from the center of the lens should the paper be?
A convex lens two focal lengths away from the paper
A concave lens two focal lengths away from the paper
A convex lens one focal length away from the paper
A concave lens one focal length away from the paper
A slide projector uses a convex lens with a focal length of 120 mm. A small picture on a transparent slide is placed upside down in the projector, 125 mm in front of the lens. What will the image on the screen look like?
Larger than the slide and right side up
Larger than the slide and upside-down
Same size as the slide and right side up
Same size as the slide and upside-down
Eyeglass lenses may be used to correct both nearsighted and farsighted vision. Someone who is farsighted has difficulty seeing tiny objects that are close to the lens. As farsighted patients look through corrective lenses toward the object, they are able to see a larger image clearly on the same side of the lens as the object. What type of lens corrects farsighted vision, and what is the orientation of the image to that of the object?
Convex; inverted
Convex; upright
Concave; inverted
Concave; upright
A copy machine has a lens with a focal length of 30 cm. How far from the lens must a document (the object) be placed if the copy (the image) is to be exactly the same size?
More than 60 cm from the lens
60 cm from the lens
Between 30 and 60 cm from the lens
30 cm from the lens
A child looks through a lens at the distant trees, and the trees still look distant but appear smaller. What type of lens is the child looking through, and is the image upright or inverted?
Convex; upright
Convex; inverted
Concave; upright
Concave; inverted
A 15-cm focal-length lens is used to focus a sharp image on a piece of paper that is 20 cm to the right of the lens. What information is known about the lens and the object?
The lens is convex, and the object is 30 cm to the left of the lens.
The lens is concave, and the object may be any distance from the lens.
The lens is convex, and the object is between 15 and 30 cm to the left of the lens.
The lens is convex, and the object is more than 30 cm to the left of the lens.
In Figure 7.2, Point "F" represents the focal point of the lens. If the candle is placed as shown in the figure, what type of image will be seen?
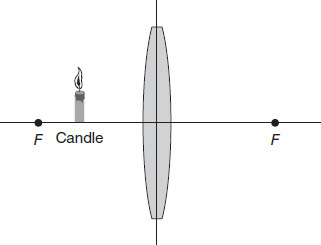
Figure 7.2
A real, inverted, smaller image
A real, inverted larger image
A virtual, upright, larger image
A virtual, upright, smaller image
1 mã đề 22 câu hỏi
1 mã đề 11 câu hỏi
1 mã đề 22 câu hỏi
1 mã đề 13 câu hỏi
1 mã đề 22 câu hỏi

