ACT Science Practice Test 2 - Multiple Choice Questions
Từ khoá: act science act practice test act science practice test 2 luyện thi act đề thi act online act multiple choice act science section act exam preparation
Bộ sưu tập: Tuyển Tập Bộ Đề Thi Đại Học Hoa Kỳ (ACT) - Có Đáp Án Chi Tiết
Số câu hỏi: 24 câuSố mã đề: 1 đềThời gian: 1 giờ
218,137 lượt xem 16,772 lượt làm bài
Comets originate from regions of our solar system that are very far from the sun. The comets are formed from debris thrown from objects in the solar system: they have a nucleus of ice surrounded by dust and frozen gases. When comets are pulled into the earth's atmosphere by gravitational forces and become visible, they are called meteors. Meteors become visible about 50 to 85 km above the surface of Earth as air friction causes them to glow. Most meteors vaporize completely before they come within 50 km of the surface of Earth.
The Small Comet debate centers on whether dark spots and streaks seen in images of the Earth's atmosphere are due to random technological noise or a constant rain of comets composed of ice. Recently, images were taken by two instruments, UVA and VIS, which are located in a satellite orbiting in Earth's magnetosphere. UVA and VIS take pictures of the aurora borealis phenomenon, which occurs in the magnetosphere. The UVA and VIS technologies provide images of energy, which cannot be seen by the human eye.
The pictures taken by VIS and UVA both show dark spots and streaks. Scientists debate whether these spots and streaks are due to a natural incident, such as small comets entering the atmosphere, or random technological noise. The layers of Earth's atmosphere are shown in Figure 1.
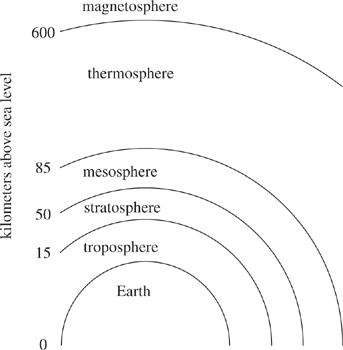
Figure 1
Two scientists debate whether there is a constant rain of comets burning up in Earth's magnetosphere.
Scientist 1
Small comets are pulled into Earth's atmosphere by gravitational effects and burn up in the magnetosphere. They are about 20 to 30 feet in diameter and burn up in the magnetosphere because they are much smaller than the comets that become meteors. Comets with larger radii will burn up in portions of the atmosphere much closer to Earth. About 30,000 small comets enter the Earth's magnetosphere every day. The dark spots and streaks on UVA and VIS images occur when the small comets begin to boil in the magnetosphere, releasing krypton and argon and creating gaseous H2O, which interacts with hydroxyl, OH-, radicals. Images taken by these instruments at different points in time show the same frequency of dark spots and streaks and give conclusive evidence in favor of the Small Comet theory. If the spots and streaks were due to random technological noise, then the frequency of their appearance would fluctuate.
Scientist 2
The dark spots and streaks in the UVA and VIS images are due to technological noise, not small comets. If the Small Comet Theory were true, and 20 small comets bombarded Earth's atmosphere per minute, there would be a visible bright object at least twice every five minutes. This is because, as objects enter the Earth's mesosphere, they burn up, creating large clouds of ice particles. As the ice particles vaporize, they have a brightness in the sky approximately equal to that of Venus. Because comets rarely enter Earth's atmosphere, such bright flashes are rare occurrences, far less than two times every five minutes, so the Small Comet theory cannot be correct. Further, since comets originate from regions of space beyond the orbit of the farthest planet, they contain argon and krypton. If the Small Comet theory were true and Earth were bombarded by 30,000 comets per day, there would be 500 times as much krypton in the atmosphere as there actually is.
According to Scientist 2, which of the following planets in our solar system is most likely the closest to the region of space where comets originate?
Jupiter
Venus
Neptune
Saturn
Based on Scientist 1’s viewpoint, a comet that burns up in the thermosphere would have a diameter of:
5-10 ft.
10-20 ft.
20-30 ft.
greater than 30 ft.
Which of the following generalizations about small comets is most consistent with Scientist 1’s viewpoint?
No small comet ever becomes a meteor.
Some small comets become meteors.
Small comets become meteors twice every five minutes.
All small comets become meteors.
During the Perseids, an annual meteor shower, more than 1 object burning up in the atmosphere is visible per minute. According to the information provided, Scientist 2 would classify the Perseids as:
typical comet frequency in the magnetosphere.
unusual comet frequency in the magnetosphere.
typical meteor frequency in the mesosphere.
unusual meteor frequency in the mesosphere.
Given the information about Earth’s atmosphere and Scientist 1’s viewpoint, which of the following altitudes would most likely NOT be an altitude at which small comets burn up?
750 km
700 km
650 km
550 km
Suppose a study of the dark holes and streaks in the UVA and VIS images revealed krypton levels in the atmosphere 500 times greater than normal levels. How would the findings of this study most likely affect the scientists’ viewpoints, if at all?
It would strengthen Scientist 1’s viewpoint only.
It would strengthen Scientist 2’s viewpoint only.
It would weaken both Scientists’ viewpoints.
It would have no effect on either Scientist’s viewpoint.
Scientist 1 would most likely suggest enhanced imaging technology that can take pictures of objects in the atmosphere be used to look at what region of the atmosphere to search for small comets?
The region between 15 km above sea level and 50 km above sea level.
The region between 50 km above sea level and 85 km above sea level.
The region between 85 km above sea level and 600 km above sea level.
The region between above 600 km above sea level.
A cotton fiber is composed of one very long cell with two cell walls. During a 2-week period of cell life called elongation, cotton fibers grow 3 to 6 cm. The level of hydrogen peroxide in cotton fiber cells during elongation is very high. Scientists wanted to study whether the level of hydrogen peroxide affected the length of the cotton fiber.
The amount of hydrogen peroxide is controlled by an enzyme called superoxide dismutase (SOD). This enzyme turns superoxide into hydrogen peroxide. Four identical lines of cotton fiber plants were created. Each line was able to express only one of three types of superoxide dismutase. The gene for SOD1 was incorporated into L1, the gene for SOD2 was incorporated into L2, and the gene for SOD3 was incorporated into L3.
Experiment
Five cotton plants of each line were grown in nutrient solution until cotton fibers completed the elongation period. The average length of cotton fibers and the average concentration of hydrogen peroxide were determined. This information is shown in Table 1.
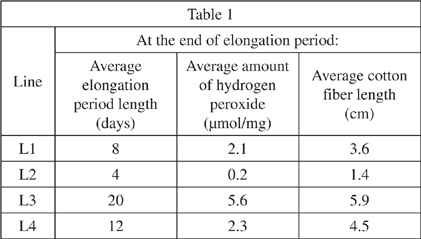
Next, because the scientists had determined the average elongation period, they measured the amount of hydrogen peroxide and the length of the cotton fibers halfway through their elongation period. This information is shown in Table 2.

Finally, the scientists measured the amount of hydrogen peroxide and the length of cotton fibers on the first day of the elongation period. This information is shown in Table 3.
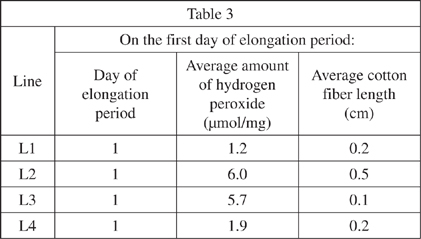
For L2, as the elongation period moved from the first day to the end, the amount of hydrogen peroxide:
increased only
decreased only
increased, then decreased
decreased, then increased
Which of the following is a dependent variable in the experiment?
The point in time during the elongation period
The type of superoxide dismutase the plant could express
The length of the cotton fiber
The type of cotton plant
A cotton fiber is one very long cell with two cell walls. A cotton fiber is a special kind of what type of cell?
Prokaryotic
Animal
Plant
Bacterial
One plant had an average cotton fiber length of 0.5 cm, and the average amount of hydrogen peroxide in its fibers was 5.9 μmol/mg. Which of the following most likely describes this plant?
It was from L1 and at the end of its elongation period.
It was from L1 and at the midpoint of its elongation period.
It was from L2 and at the beginning of its elongation period.
It was from L2 and at the end of its elongation period.
The scientists used one of the four lines of cotton plants as a control. Which line was most likely the control?
L1
L2
L3
L4
Suppose the data for all the plants were plotted on a graph with the time of the elongation period on the x-axis and the average length of the cotton fiber on the y-axis. Suppose also that the best-fit line for these data was determined. Which of the following would most likely characterize the slope of this line?
The line would have a positive slope.
The line would have a negative slope.
The line would have a slope equal to zero.
The line would have no slope, because the line would be vertical.
Convection is a heat transfer process caused by moving liquid or gas currents from a hot region to a cold region. As a liquid or gas cools, it gets more dense. An example of a convection process is a cup of hot coffee: the liquid toward the top is cooled by the air, so it becomes more dense and sinks to the bottom of the cup; the hotter liquid toward the bottom of the cup is less dense, so it rises toward the top. See Figure 1, below.
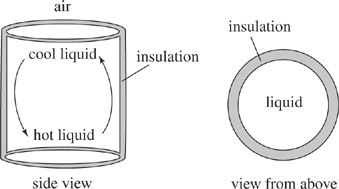
Figure 1
The temperature of the liquid at the hot end of the insulated system is higher than the temperature at the cool end of the system. The difference (ΔT) between the hot liquid at the bottom and the cold liquid at the top changes depending on the starting temperature of the system. Table 1 gives ΔT for 500 mL of water in an insulated container with a height of 6.0 cm and a cross-sectional area of 4.0 cm2 when the container is heated to different temperatures.
| Table 1 | |
| Heated temperature (°C) | ΔT (°C) |
| 80 | 1 |
| 100 | 4 |
| 120 | 10 |
| 140 | 19 |
Figure 2 shows how ΔT changes with cross-sectional area for 500 mL of 100°C water in a container with a height of 6.0 cm. Figure 3 shows how ΔT changes with height for 500 mL 100°C water in a container with a cross-sectional area of 4.0 cm2.
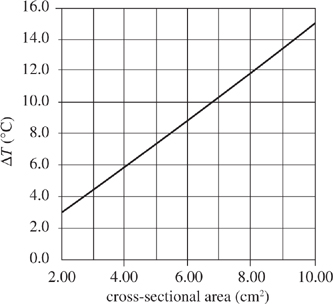
Figure 2

Figure 3
System 1 and System 2 are two convection systems. Based on
Figure 2, if System 1 were the same height as System 2, but had two times the cross-sectional area and the systems were heated to the same temperature, the ratio of ΔT for System 1 to ΔT for System 2 would be:
1:01
1:02
2:01
3:01
For the systems described in the passage, if the containers were metal containers rather than insulated containers, heat would be transferred from the water to the container by which of the following heat transfer processes?
I. Convection
II. Conduction
III. Radiation
I only
II only
I and III only
I and II only
Which of the following systems, if all were heated to the same temperature, would have the greatest ΔT?

Based on the information in
Table 1, if an insulated container of 500 mL of water with a height of 6.0 cm and a cross-sectional area of 4.0 cm2 were heated to 120°C, which of the following pairs could represent the temperatures of the liquid at the top and bottom ends of the container?
Bottom endTop/Exposed to air end
140°C 120°C
140°C 110°C
115°C 115°C
120°C 110°C
The data in the passage supports the hypothesis that ΔT increases as which of the following increases?
Amount of insulation
Volume of liquid
Radius of the container
Air temperature
Metallic alloys, solid mixtures of metal, are useful for coin production when they contain a high percentage of zinc. When electric current is applied to zinc in the presence of precious metal solutions of silver nitrate, copper sulfate or potassium gold cyanide, the precious metals plate (form a coating) on the zinc surface.
- Silver nitrate, formed when silver dissolves in nitric acid, reacts with zinc to form solid silver and zinc nitrate.
- Copper sulfate, formed when copper dissolves in sulfuric acid, reacts with zinc to form solid copper and zinc sulfate.
- Potassium gold cyanide contains reactive gold ions.
A chemist performed experiments on precious metal plating.
Experiment 1
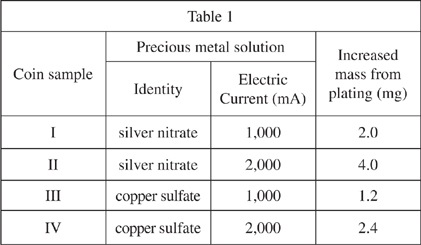
The chemist obtained 4 coin-like samples of a high percentage zinc alloy. All samples were circular, had a radius of 1 cm, and had the same thickness. The mass of each coin was recorded. Each coin was wired via a battery to a strip of either pure silver or copper metal. Coins wired to silver were placed in dilute nitric acid and coins wired to copper were placed in dilute sulfuric acid. Electric current of either 1,000 milliamperes (mA) or 2,000 mA was applied for 30 minutes to each sample. The coins were removed and the increase in mass from precious metal plating was recorded in milligrams. Results of the experiment are shown in Table 1.
Experiment 2
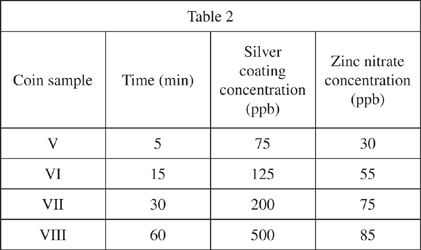
The chemist completely dissolved equal amounts of pure silver in 4 beakers of nitric acid. He then placed equivalent coin-like samples of zinc into the beakers for different lengths of time measured in minutes (min). The coin surfaces developed a silver metal coating without any electric current applied. The concentrations of silver coating on the coin and zinc nitrate in the surrounding solution were determined in parts per billion (ppb) and recorded in Table 2.
A comparison of the results for coin samples II and IV supports the hypothesis that zinc is plated more extensively when exposed to:
silver nitrate and a current of 1,000 mA than silver nitrate and a current of 2,000 m
copper sulfate and a current of 1,000 mA than copper sulfate and a current of 2,000 m
silver nitrate than when exposed to copper sulfate.
copper sulfate than when exposed to silver nitrate.
If the chemist were to repeat Experiment 1, but compress each coin sample to a radius of 0.5 cm to decrease the surface area exposed to the surrounding solution, how would the mass of precious metal plated most likely be affected?
The mass of precious metal plated would decrease for all coin samples.
The mass of precious metal plated would decrease for coin samples I and III and increase for coin samples II and I
The mass of precious metal plated would remain constant for all coin samples.
The mass of precious metal plated would increase for all coin samples.
According to the information in the passage, a zinc alloy coin sample exposed to which of the following conditions would result in the greatest concentration of zinc nitrate?
10 minutes in a solution with a high initial concentration of silver nitrate
10 minutes in a solution with a low initial concentration of silver nitrate
6 minutes in a solution with a high initial concentration of silver nitrate
6 minutes in a solution with a low initial concentration of silver nitrate
In Experiment 1, if the chemist had applied 1,580 mA to a 1 cm radius zinc alloy coin sample in a copper sulfate solution, approximately how much copper would have plated after 30 minutes?
0.6 mg
1.1 mg
1.9 mg
4.6 mg
In Experiment 1, which of the following variables was the same for all 4 zinc alloy coin sample trials?
Change in mass from plating
Electric current applied
Type of precious metal solution used
Initial radius of the sample
According to the passage, if a chemist wants to study the effect of plating zinc alloys with silver, the chemist should monitor the concentration of which of the following substances in the surrounding solution?
Potassium gold cyanide
Zinc nitrate
Copper sulfate
Sulfuric acid
1 mã đề 22 câu hỏi
1 mã đề 11 câu hỏi
1 mã đề 22 câu hỏi
1 mã đề 13 câu hỏi
1 mã đề 22 câu hỏi

