ACT Science Practice Test 17
Bộ sưu tập: Tuyển Tập Bộ Đề Thi Đại Học Hoa Kỳ (ACT) - Có Đáp Án Chi Tiết
Số câu hỏi: 29 câuSố mã đề: 1 đềThời gian: 1 giờ
219,654 lượt xem 16,885 lượt làm bài
Organic molecules (carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids) compose and are produced by living organisms. Scientists believe that simple organic molecules originally formed from inorganic molecules on primitive Earth. This step is considered a key precursor to the development of life on our planet. Two leading theories on the origin of the first organic molecules are described here.
Primordial Soup
The theory that organic molecules formed in the atmosphere of primitive Earth using energy from lightning is often called the "primordial soup theory." Evidence for this theory includes the Miller-Urey experiment, in which the conditions believed to exist in the primitive atmosphere were reproduced to create organic molecules.
The major components of the primitive atmosphere were believed to be methane (CH4), ammonia (NH3), hydrogen (H2), and water (H2O). These gases were put into a closed system and exposed to a continuous electrical charge to simulate lightning storms. After one week, samples taken from the apparatus contained a variety of organic compounds, including some amino acids (components of proteins). Figure 4.1 is a diagram of the apparatus used in the Miller-Urey experiment.
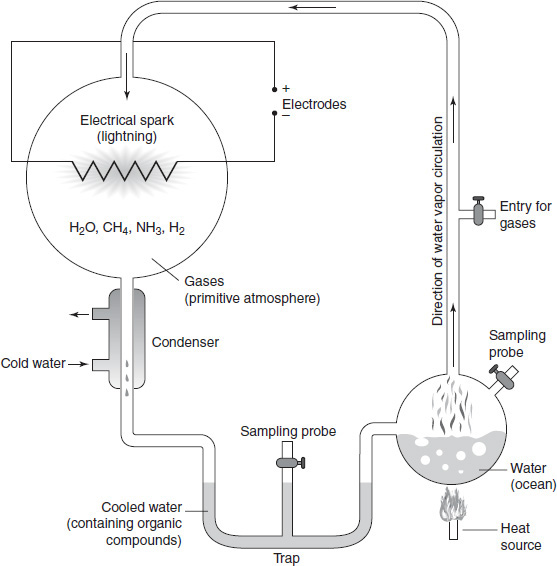
Figure 4.1
Hydrothermal Vents
The theory that organic molecules originally formed in the deep oceans using energy from inside the earth focuses on the existence of hydrothermal vents. Evidence for this theory includes the fact that ecosystems of diverse organisms have been found to exist around hydrothermal vents in the deep ocean. These ecosystems thrive without any energy input from the sun.
Organic molecules are only stable within a very narrow temperature range. Hydrothermal vents release hot (300°C) gases originating from inside the earth into the otherwise cold (4°C) water of the deep ocean. This release of gases causes a temperature gradient to exist around deep-sea vents. Scientists believe that within this temperature gradient exist the optimal conditions to support the formation of stable organic compounds. Figure 4.2 shows a diagram of the gradient produced by deep-sea vents.
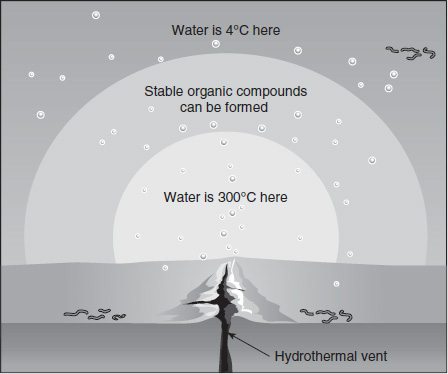
Figure 4.2
Which of the following is not an organic molecule?
Carbohydrates
Water
Lipids
Nucleic acids
Both theories on the origin of organic molecules are based on the assumption that those molecules:
contain different atoms than inorganic molecules.
only exist in the atmosphere and deep ocean.
have not yet been produced in the laboratory.
can be produced from inorganic molecules.
In Figure 4.1, the purpose of the heat source is to:
produce water vapor for the simulated atmosphere.
simulate hydrothermal vents in the deep ocean.
reduce inorganic compounds to organic compounds.
generate an electrical charge to stimulate the reaction.
Ammonia (NH3) is an:
inorganic compound.
element.
amino acid.
organic compound.
In Figure 4.1, the reaction that produces organic molecules occurs in which part of the Miller-Urey apparatus?
Condenser
Large sphere
Trap
Small sphere
Based on the hydrothermal vents theory, which of the following would most likely be the optimal temperature range for organic molecule formation?
Between 0°C and 4°C
Higher than 300°C
Lower than 300°C
Between 4°C and 25°C
Which of the following statements would scientists supporting either theory most likely agree on?
At least some organic compounds on Earth likely originated in meteorites from space.
The production of amino acids requires the existence of a temperature gradient.
The existence of water on Earth was essential to the original formation of organic compounds.
A single method most likely produced the original versions of all organic molecules.
The specific source of energy used to form simple organic molecules is:
addressed in the primordial soup theory only.
not discussed in either of the two theories.
a major difference between the two theories.
the only similarity between the two theories.
According to the primordial soup theory, which of the following gases is not believed to have been a major component of the primitive atmosphere?
Methane
Hydrogen
Water vapor
Helium
The greatest limitation in the design of the Miller-Urey experiment is the:
use of a condenser to cool water vapor.
production of a variety of organic compounds.
presence of a constant electrical charge.
recycling of water throughout the apparatus.
The hydrothermal vents theory states that organic molecules originally formed:
inside the earth.
in the earth's atmosphere.
in the deep ocean.
within volcanoes.
Scientists consider the outcome of the Miller-Urey experiment to be evidence:
that refutes the primordial soup theory.
in support of the primordial soup theory.
that refutes both the primordial soup and the hydrothermal vents theories.
in support of the hydrothermal vents theory.
According to the passage, temperature gradients exist in the deep ocean due to the:
constant release of hot gases into cold water.
decreased availability of sunlight at greater depths.
existence of ecosystems made up of diverse organisms.
reactions that produce organic molecules.
Which of the following is a key assumption of the primordial soup theory?
Sunlight provided the energy needed to convert inorganic compounds to organic compounds.
The composition of the primitive atmosphere was different than that of the current atmosphere.
Amino acids can be produced from inorganic compounds in the laboratory.
Organic compounds can only be produced by the reaction of other organic compounds.
As a liquid evaporates, the vapors on the surface of the liquid exert a vapor pressure. Vapor pressure varies with the liquid's temperature.
When vapor pressure equals the surrounding atmospheric pressure, boiling occurs. The normal boiling point of a liquid is defined as the temperature at which vapor pressure is equal to the standard atmospheric pressure of 760 mmHg (1 atm). If atmospheric pressure changes, a liquid's boiling point will also change.
Figure 4.3 illustrates the relationship between vapor pressure and temperature for four organic compounds belonging to the alkane group. The normal boiling point is indicated by a horizontal dashed line.
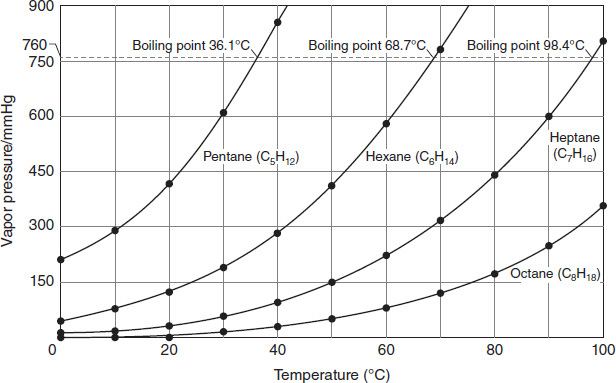
Figure 4.3
Source: http://wiki.chemprime.chemeddl.org.
Organic compounds are composed of various functional groups attached to a hydrocarbon backbone. A functional group is a specific grouping of atoms that exhibits a characteristic set of properties. These properties remain consistent, regardless of the overall size of the compound.
Figure 4.4 compares the normal boiling points of organic compounds of increasing size for eight different functional groups, including the alkane group.
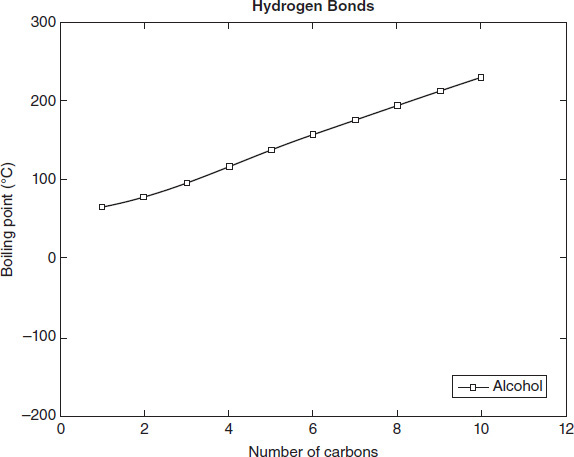
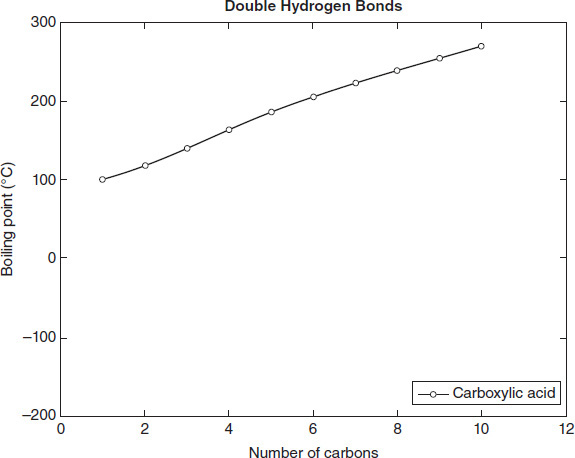
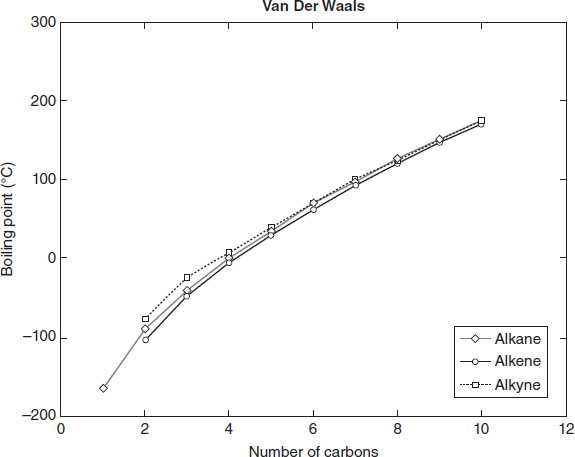
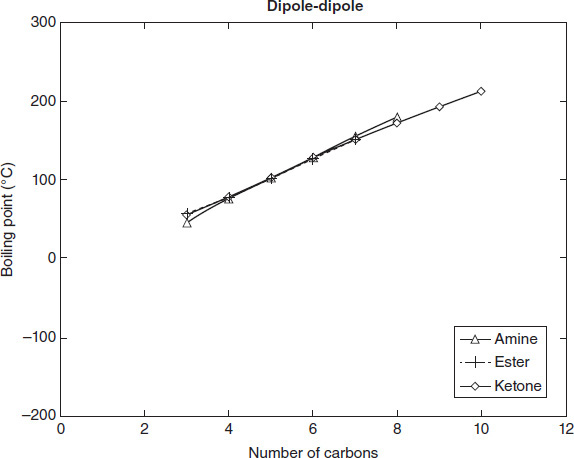
Figure 4.4
Table 4.1 lists the types of chemical bonds each of the eight functional groups are capable of forming. Stronger bonds are more difficult to break, thus requiring a higher temperature for phase changes.
TABLE 4.1 Functional Group Bonds
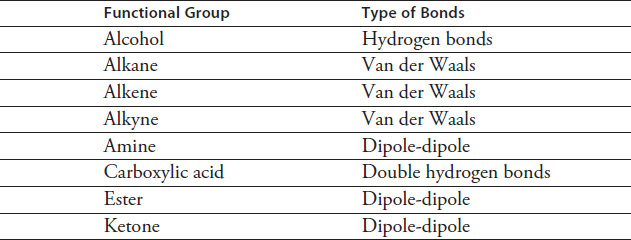
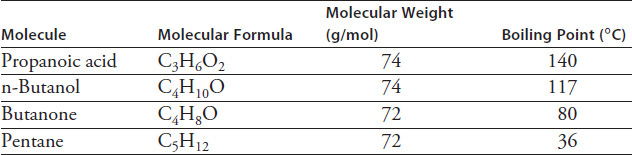
Table 4.2 lists characteristics of four common organic compounds with similar molecular weights. The temperatures listed represent the normal boiling point for each molecule.
TABLE 4.2 Molecular Weight
A compound's normal boiling point is the:
minimum temperature at which the compound boils.
average temperature at which the compound boils across all possible atmospheric pressures.
maximum temperature at which the compound boils.
temperature at which the compound boils under standard atmospheric pressure.
According to Figure 4.3, an organic compound will boil at a lower temperature if:
vapor pressure increases.
atmospheric pressure decreases.
atmospheric and vapor pressures become unequal.
vapor pressure is greater than atmospheric pressure.
At a vapor pressure of 50 mmHg, which alkane in Figure 4.3 would boil closest to 0°C?
Heptane
Hexane
Pentane
Octane
According to Figure 4.3, what vapor pressure will cause pentane's boiling point to be closest to 40°C?
760 mmHg
600 mmHg
400 mmHg
850 mmHg
What is the best approximation for the normal boiling point of octane in Figure 4.3?
126°C
100°C
145°C
98°C
According to Figure 4.4, the alkanes exhibit normal boiling points most similar to which other group?
Alkynes
Alcohols
Carboxylic acids
Amines
Based on the data in Figure 4.4, a 2-carbon alcohol would exhibit a normal boiling point closest to that of a:
3-carbon alkane.
9-carbon alkene.
4-carbon ketone.
2-carbon carboxylic acid.
Based on the data in Figure 4.4, which type of bond listed in Table 4.1 is the weakest?
Dipole-dipole
Double hydrogen
Van der Waals
Single hydrogen
Caproic acid is a carboxylic acid with a molecular formula of C6H12O2. Which of the following temperatures is closest to the normal boiling point of caproic acid?
200°C
250°C
100°C
125°C
Based on the data in Figure 4.4, which of the following lists the bonds in Table 4.1 from the highest to the lowest boiling point required to break them?
Van der Waals, dipole-dipole, single hydrogen, double hydrogen
Double hydrogen, single hydrogen, dipole-dipole, Van der Waals
Single hydrogen, double hydrogen, dipole-dipole, Van der Waals
Dipole-dipole, Van der Waals, single hydrogen, double hydrogen
Which of the following generalizations about the relationship between an organic compound's molecular weight and its boiling point is best supported by the data in Table 4.2?
The boiling point varies directly with molecular weight.
As molecular weight increases, the boiling point decreases.
As molecular weight decreases, the boiling point increases.
The boiling point is not determined by molecular weight.
Based on the data in Figure 4.4, n-Butanol (see Table 4.2) most likely contains which functional group?
Alcohol
Ester
Amine
Alkyne
Which of the four compounds in Table 4.2 is most likely to contain double hydrogen bonds?
Pentane
Butanone
Propanoic acid
n-Butanol
Based on the information in the passage, which of the following can be inferred about the type of bonds in an organic compound?
Double hydrogen bonds are easier to break at high temperatures than single hydrogen bonds.
Dipole-dipole bonds require the highest boiling point to break of all four types of bonds.
Van der Waals bonds become easier to break as a compound's vapor pressure is increased.
At the same vapor pressure, single hydrogen bonds require a higher boiling point to break than dipole-dipole bonds.
Which of the following generalizations is best supported by the data in Figures 4.3 and 4.4?
Organic compounds containing the same number of carbon atoms have similar boiling points.
The boiling point increases with the number of carbon atoms among organic compounds within the same group.
The number of carbon atoms in an organic compound cannot be used to predict the compound's relative boiling point.
The greater the number of carbon atoms in an organic compound, the lower that compound's boiling point is.
1 mã đề 22 câu hỏi
1 mã đề 11 câu hỏi
1 mã đề 22 câu hỏi
1 mã đề 13 câu hỏi
1 mã đề 22 câu hỏi

